|
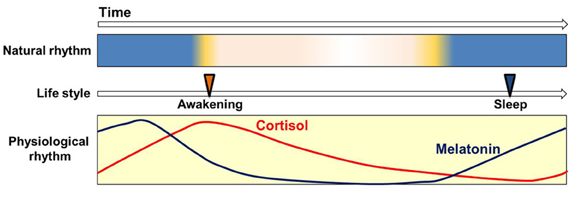
As part of my Health and Longevity program I focus a significant amount of time on sleep. Poor sleep is associated with an increased risk of chronic health problems such as cancer, obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Prior to light bulbs people slept an average of 10 hours a night. Now the typical American gets less then seven hours of sleep. Ideally, we need 7.5 to 8 hours of sleep per night. One of the contributors to poor sleep is the use of artificial lighting and especially electronics at night. Devices, such as our phones and computers, are programmed to emit high levels of blue light in order to mimic the light wavelengths associated with sunlight. This type of light helps us feel alert and suppresses our natural melatonin production. As can be seen from the illustration below melatonin begins to rise when the sun sets which is when orange light predominates and blue light wavelengths dissipate. Simultaneously, our cortisol hormones decrease during sleep and begin to rise when we need to awaken. Melatonin helps us feel drowsy and cortisol helps feel alert. How does our body respond to blue light?
Interestingly, the Ganglion (nerves) in the back of our eye respond to blue light. When the amount of blue light decreases (dusk) this is transmitted from the nerve to the Pineal gland which secrets melatonin. Melatonin suppresses adrenal function and the release of cortisol which helps decrease alertness. With an decrease in cortisol we also get activation of the immune system. Finally, what are some practical ways to reduce your exposure to blue light at night? 1. One hour before bedtime: Turn off or dim all lights after sunset and avoid watching TV or using light emitting electronics. Research indicates that using an electronic device within one hour of bedtime can delay falling asleep for more than an hour. Another study showed that: Compared to dim light, exposure to room light before bedtime suppressed melatonin, resulting in a later melatonin onset in 99.0% of individuals and shortening melatonin duration by about 90 min. Also, exposure to room light during the usual hours of sleep suppressed melatonin by greater than 50% in most (85%) trials. This could mean it could take even more time before you are able to fall asleep. 2. After sundown, shift to low-wattage yellow bulbs. You can also install programs on your computer or phone, like f.lux, that reduce the blue wavelengths at sunset. 3. Amber colored glasses: The easiest solution may be to simply use amber colored glasses that block blue light. Studies indicate that these glasses are effective ways to not impairment melatonin production even in the presence of significant light. If the above techniques don't help and you have a sleep problem related to other factors feel free to reach out to me for a consultation.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Doctor/Telemed/Sick Visit $60
PREMIUM $45-60/MO
WEIGHT LOSS $60 HCG DIET $399 HORMONE VISIT $60 BLOOD WORK $60 LACERATION $150 STEM CELL $999 Testosterone Visit $69 Vitamin B12 $25 Archives
June 2022
Categories
All
|